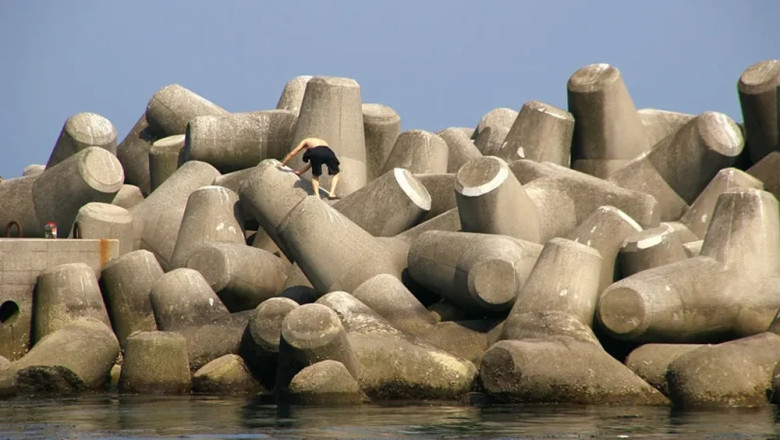

Strange Structures on the Seacoast
Introduction to Tetrapods
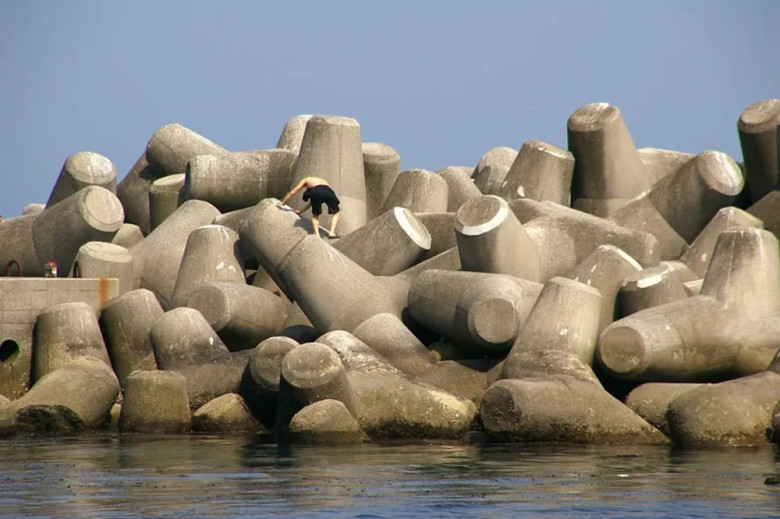

Have you ever walked along the seashore and noticed odd concrete structures dotting the landscape? These enigmatic formations are called tetrapods, and they might not be as random as you think. Designed with four conical arms, each tetrapod is engineered for a purpose: coastal protection. They have become a common sight along coastlines around the world, standing as silent guardians against the relentless force of waves while also adding a unique aesthetic to coastal vistas.
History of Tetrapods

Tetrapods were conceived in the 1950s, post-World War II, as a response to the rising need for coastal defenses. Their design, characterized by four interconnected arms, improves stability and resistance against high-energy waves. Unlike remnants from war, tetrapods embody a modern approach to engineering, merging functionality with practicality. Their evolution marks a significant advancement in how societies interact with their coastline, transitioning from military structures to essential protective measures against erosion.
Purpose of Tetrapods

The primary function of tetrapods is to serve as breakwaters, designed to mitigate wave energy and protect coastlines from erosion. By dissipating the power of incoming waves, they help to preserve beach areas and reduce the impact of storm surges. Additionally, their structure promotes sedimentation, aiding in the natural replenishment of beaches. This multifaceted approach to coastal management underscores their importance in protecting property and maintaining the natural shoreline.
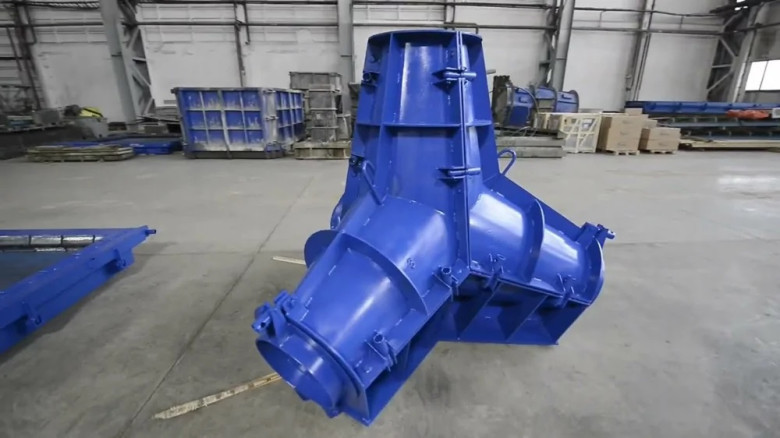
Construction of Tetrapods
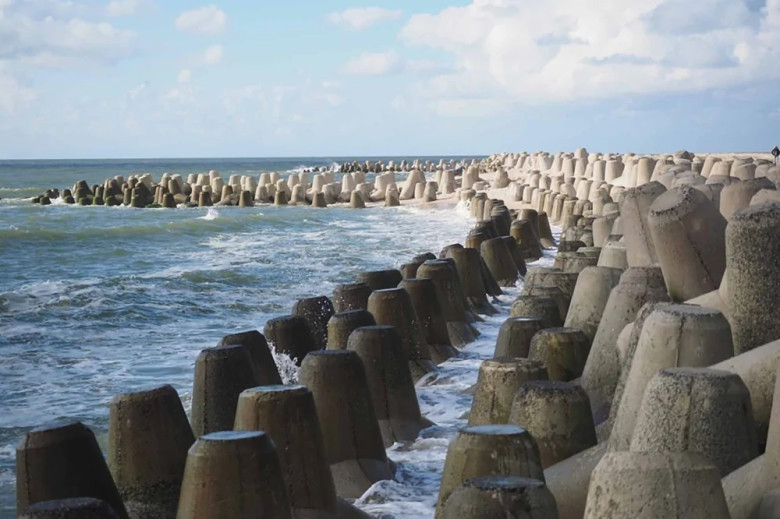

Tetrapods are crafted from high-quality hydraulic concrete, known for its durability in marine environments. This concrete is specifically engineered to withstand constant exposure to water and the temperature extremes often found at the coast. Weighing several tons, the immense weight of each tetrapod ensures stability against harsh sea conditions. Construction is carried out in specialized facilities where precision and quality control take precedence, ensuring that each unit fulfills its coastal protection mandate effectively.
Placement and Arrangement
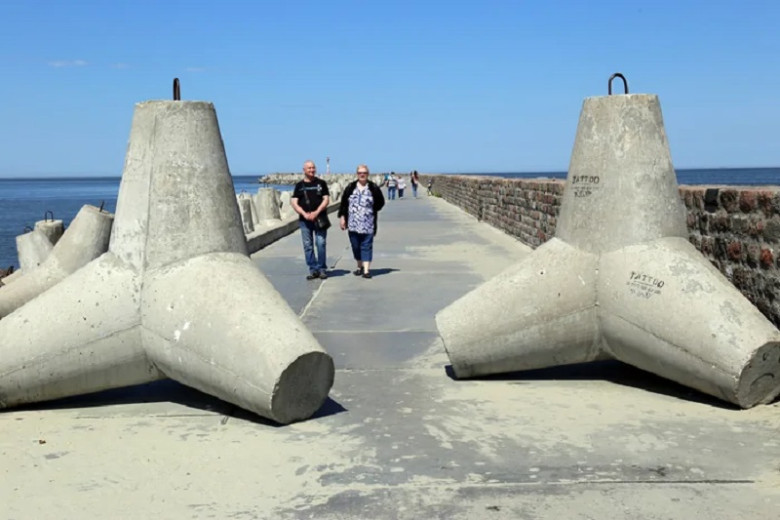

Strategically placed along coastlines, tetrapods are arranged in specific patterns to maximize their protective capabilities. This arrangement promotes wave dissipation while minimizing potential disturbances in the natural flow of water. Their placement is determined by various factors, including local wave patterns, storm surge history, and the specific geography of the shoreline. The careful planning behind their positioning underscores the importance of engineering in managing coastal ecosystems.
Variation in Coastal Structures
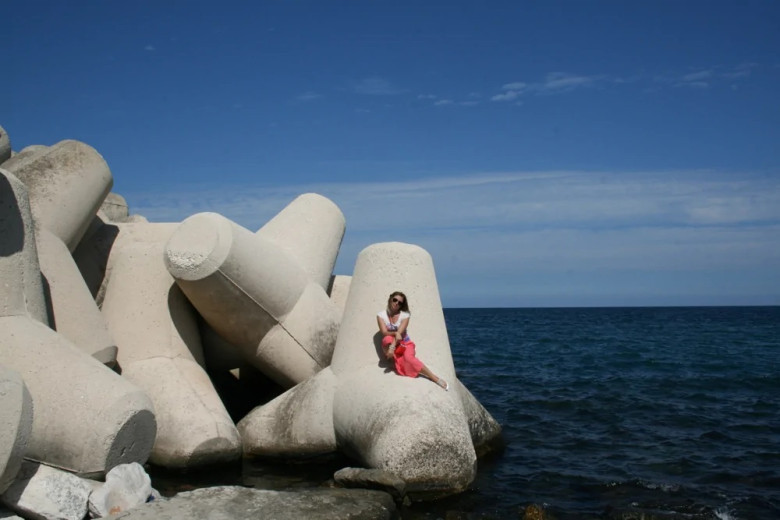

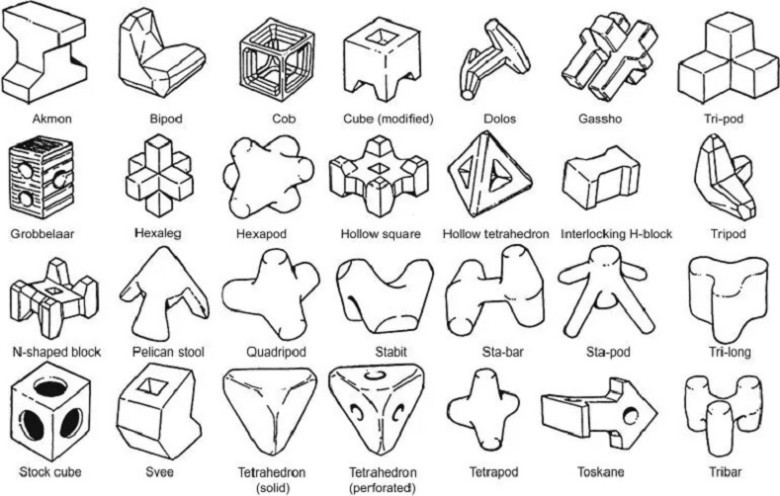
While tetrapods are prevalent in many regions, they are just one part of a broader array of coastal protective structures. In addition to tetrapods, engineers employ tetrahedrons, commonly known as "dragon's teeth," and other formations to create effective breakwaters. Each structure serves unique purposes, with adaptations based on local geography and conditions. Understanding this diversity is crucial when exploring coastal resilience strategies and their implications for environmental management.
Tetrapods Around the World

Tetrapods are used worldwide, from the shores of Japan to the beaches of Europe and North America. Each region utilizes them according to specific coastal needs, adapting their implementation to local conditions. For instance, in Japan, tetrapods are vital for tsunami protection, while in Europe, they help reclaim sandy beaches from erosion. This global perspective highlights how different cultures manage their coastlines and the universal importance of protecting seaside environments.
Environmental Impact

Though tetrapods are essential for coastal defense, they can also have environmental repercussions. Their placement can alter local ecosystems, affecting marine habitats and sediment dynamics. Engineers strive to minimize the ecological impact by conducting thorough environmental assessments before installation. Sustainable practices, including designing tetrapods to promote marine life and enhance beach habitats, are increasingly integrated into the planning process to support both human and environmental needs.
The Aesthetics of Tetrapods

Beyond their practical functions, tetrapods have gained an aesthetic identity of their own. Their unique shape and arrangement create visually intriguing coastal landscapes that attract photographers and nature enthusiasts alike. Many coastal communities have embraced the presence of tetrapods, incorporating them into public art projects or using them to enhance recreational areas. This blend of utility and aesthetic value showcases how human ingenuity can harmonize with nature.
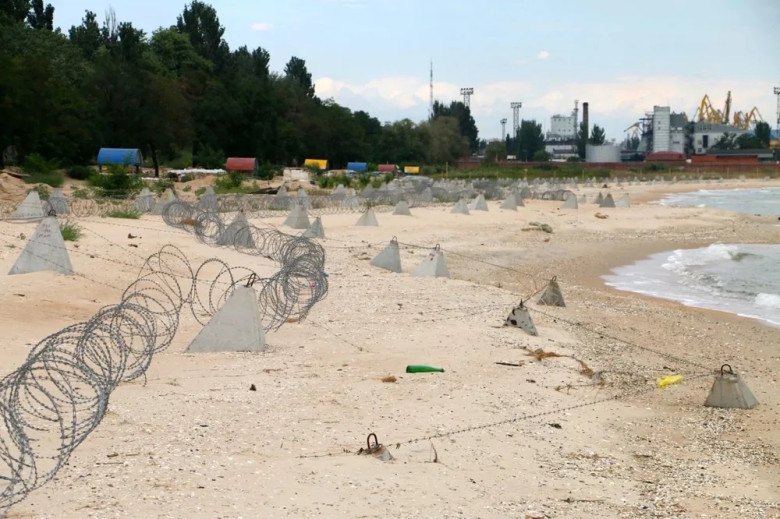
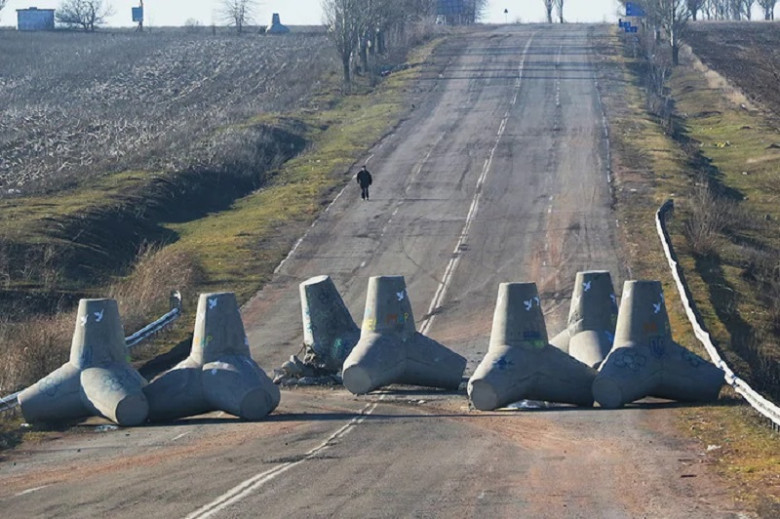
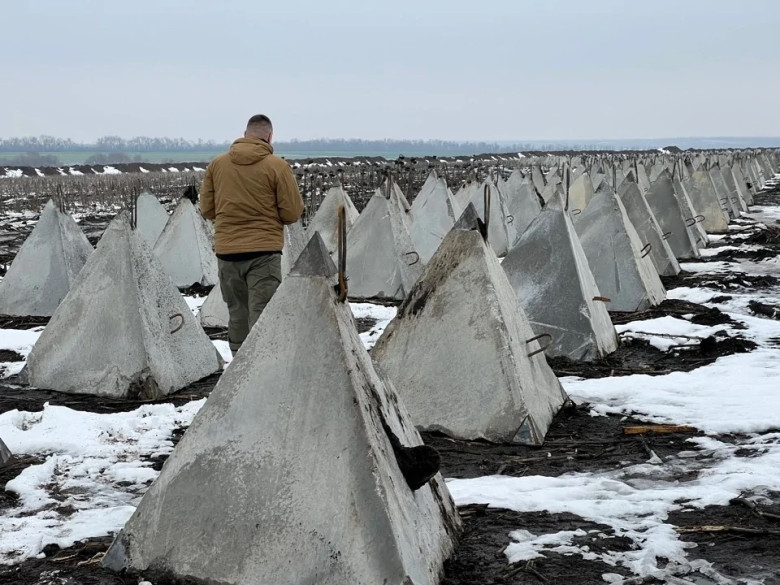
Tetrapods and Military Use

Surprisingly, tetrapods have found utilization beyond coastal protection. During military engagements, such as the conflict in Donbass in 2014, these structures were repurposed as barriers to impede enemy advancement. Their significant weight made them effective in blocking vehicle pathways, demonstrating their versatility. However, this dual-use underscores the importance of understanding the broader implications of coastal infrastructure in various contexts, including security and defense.
Notable Installations

Several notable installations of tetrapods exist around the world. In the Netherlands, extensive use of tetrapods is part of the country's robust flood defense system. Similarly, in the Caribbean, tetrapods protect against hurricanes, highlighting their resilience. These examples illustrate how specific regions adapt tetrapod deployments based on local climates and threats, showcasing the vital role they play in global coastal management strategies.
Maintenance and Lifespan
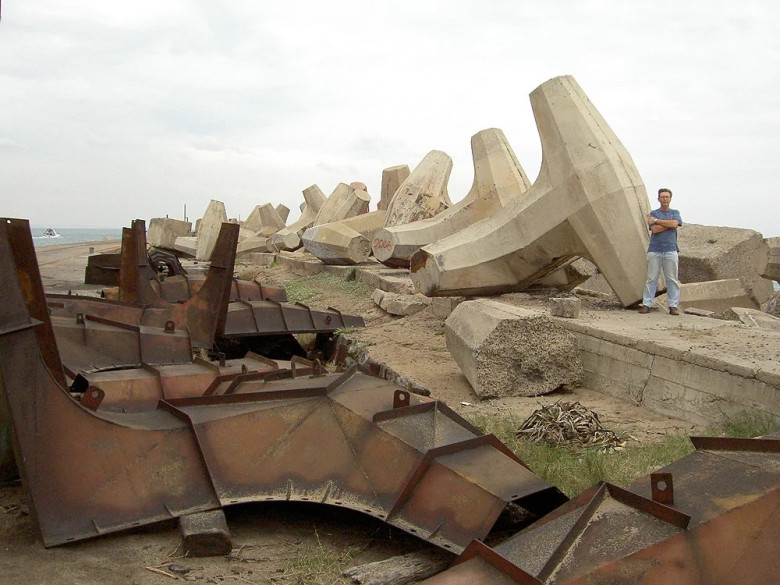

Maintaining tetrapods is crucial to ensuring their long-term effectiveness. Regular inspections assess wear from wave action and weather conditions, while repairs or replacements may be necessary after extreme weather events. Their anticipated lifespan can vary, but with proper care, tetrapods can last for decades, serving their protective purpose while contributing to coastal stability. Understanding maintenance practices is vital for communities relying on these structures.
Tetrapods in Scientific Research
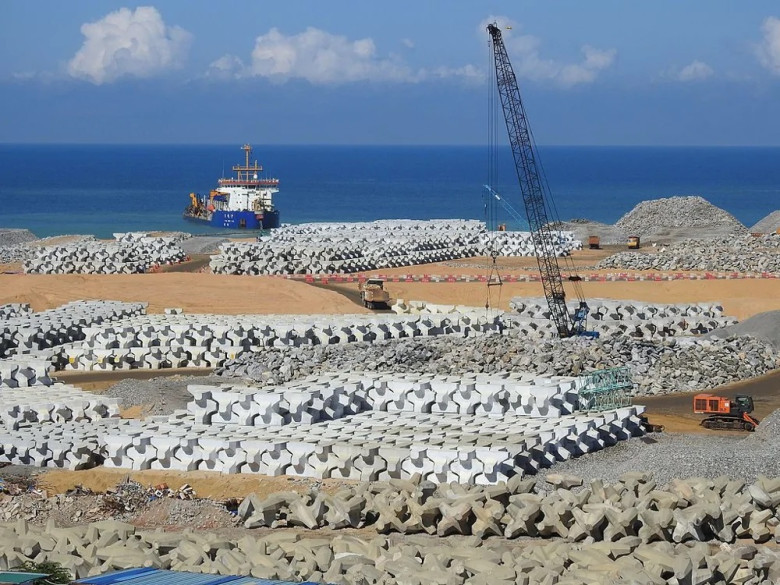

Tetrapods have garnered attention from scientists interested in coastal dynamics and engineering. Researchers study their effectiveness in wave attenuation and sediment transport, yielding valuable data that inform future designs and deployments. Insights gained from evaluating tetrapod performance enhance our understanding of wave interactions and coastal resilience, contributing to advancements in marine engineering practices and environmental management.
Climate Change Considerations
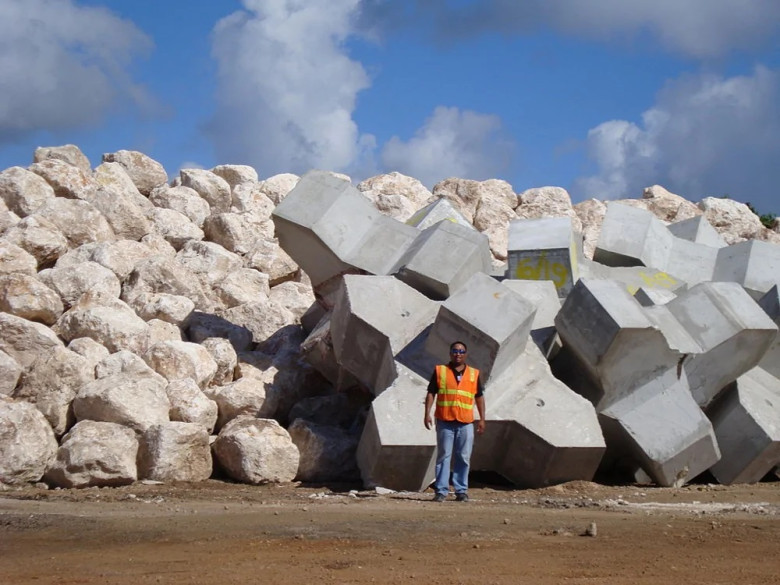

As climate change increases the frequency of extreme weather events, the role of tetrapods becomes even more critical. Rising sea levels and increased storm intensity intensify the erosion of coastlines, necessitating effective protective structures like tetrapods. Adapting existing strategies to account for the changing climate will be vital for their future relevance, connecting engineering with ecological resilience to safeguard coastal environments.
Local Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in discussions about tetrapod placement and maintenance fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Community involvement can drive educational initiatives about coastal protection, enhancing public understanding of their importance. Furthermore, listening to local concerns can lead to improved decision-making regarding coastal management, balancing the needs of residents with environmental considerations for sustainable development.
Conclusion and Future Outlook

In conclusion, tetrapods are fascinating structures serving crucial roles in coastal protection worldwide. As engineering evolves and climate challenges increase, their effectiveness must be continuously assessed and adapted. Future innovations may enhance tetrapod designs, promote environmental sustainability, and engage communities in protective strategies. Recognizing the importance of these unique coastal features ensures that we protect our shorelines for generations to come.












Comments
0 comment